深度学习之图像分类(六)Inception进化史
本节学习Inception 进化历史,感受 Inception 进化中使用的思想,其中学习描述部分参考 大话CNN经典模型:GoogLeNet(从Inception v1到v4的演进)。
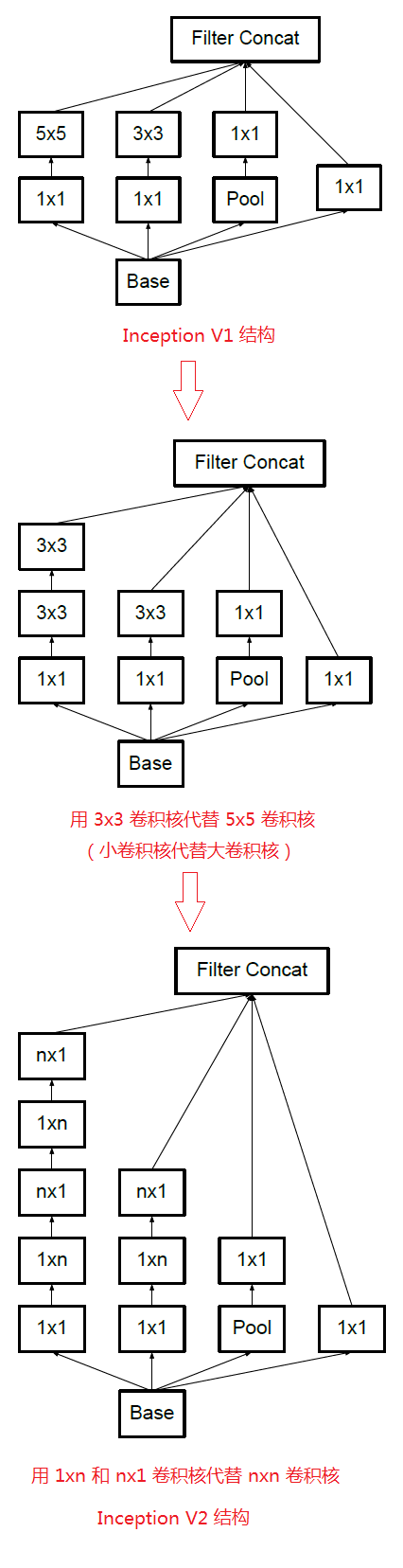
1. Inception V1
在上一讲 GoogLeNet网络结构 中我们学习了原始的 Inception,作为一种“基础神经元”结构,用来搭建一个稀疏性、高计算性能的网络结构。
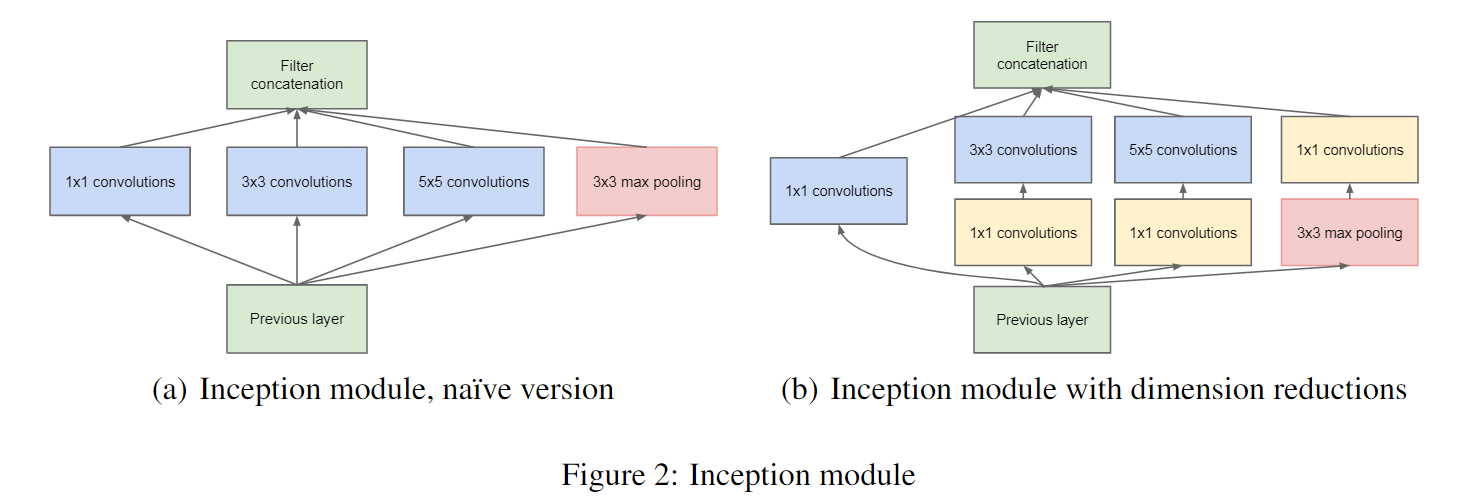
在上图(a)中,将特征矩阵输入四个分支进行处理,再将处理结果拼接成输出特征矩阵。需要注意的是:每个分支所得到的特征矩阵的高和宽必须相同,否则我们没办法按照通道进行拼接。在上图(b)中,加上了三个 $1 \times 1$ 卷积层进行降维处理。注意,在 Inception 的 Maxpool 中 stride = 1,也就是保特征图大小的池化操作。该结构将 CNN 中常用的卷积(1x1,3x3,5x5)、池化操作(3x3)堆叠在一起(卷积、池化后的尺寸相同,将通道相加),一方面增加了网络的宽度,另一方面也增加了网络对尺度的适应性。
对此,我的额外理解是:三个尺度的感受野某种程度上对应于特征提取中的尺度不变性?
2. Inception V2
GoogLeNet 凭借其优秀的表现,得到了很多研究人员的学习和使用,因此 GoogLeNet 团队又对其进行了进一步地发掘改进,产生了升级版本的 GoogLeNet。GoogLeNet 设计的初衷就是要又准又快,而如果只是单纯的堆叠网络虽然可以提高准确率,但是会导致计算效率有明显的下降,所以如何在不增加过多计算量的同时提高网络的表达能力就成为了一个问题。Inception V2 版本的解决方案就是修改 Inception 的内部计算逻辑,提出了比较特殊的“卷积”计算结构。GoogLeNet V2 的原始论文为 Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision
2.1 卷积分解(Factorizing Convolutions)
GoogLeNet 与 VGGNet 是同一年发表的,在 Inception V2 中,吸取了 VGGNet 提出的堆叠卷积核可以替代大卷积核的思想,在保持感受野不变的情况下,减少参数量,降低学习难度。比如 5x5 卷积核的参数有 25 个, 3x3 卷积核的参数有 9 个,前者是后者的 25/9=2.78 倍。用 2 个连续的 3x3 卷积层组成的小网络来代替单个的 5x5 卷积层,在保持感受野范围的同时又减少了参数量。
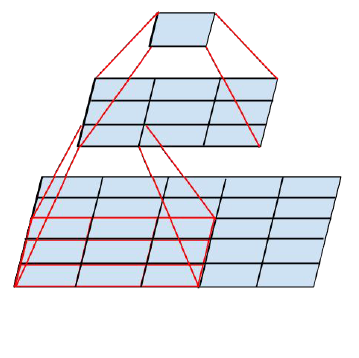
通过大量实验表明,这种替代方案并不会造成表达缺失。可以看出,大卷积核完全可以由一系列的 3x3 卷积核来替代,那能不能再分解得更小一点呢?GoogLeNet团队考虑了 nx1 的卷积核,如下图所示,用两个正交方向的 3x1 取代 3x3 卷积:
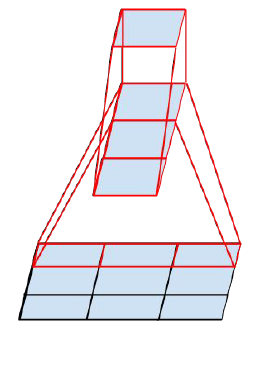
因此,任意 nxn 的卷积都可以通过 1xn 卷积后接 nx1 卷积来替代。GoogLeNet 团队发现在网络的前期使用这种分解效果并不好,在中度大小的特征图(feature map)上使用效果才会更好(特征图大小建议在 12 到 20 之间)。
基于上述分析,我们得到了下图进化历史:
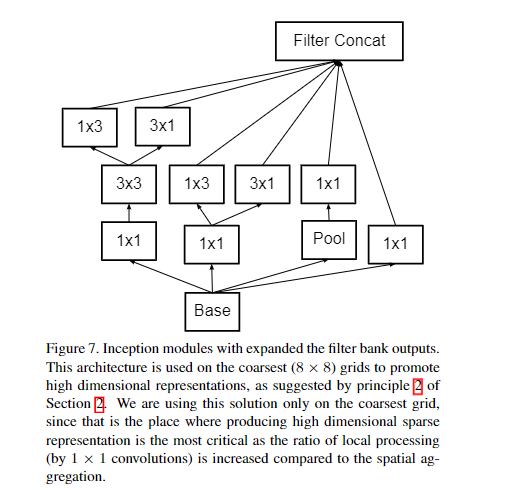
还有一个变种如图所示:
2.2 降低特征图大小
一般情况下,如果想让图像缩小,可以有如下两种方式:
-
先对特征图做池化 pooling,再做 inception
-
先对特征图做 Inception,再做池化 pooling
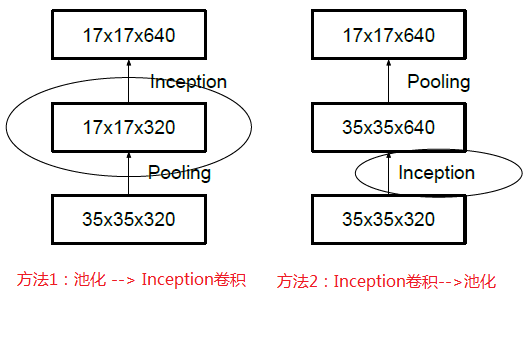
但是方法一(左图)先作pooling(池化)会导致特征表示遇到瓶颈(特征缺失),方法二(右图)是正常的缩小,但计算量很大。为了同时保持特征表示且降低计算量,将网络结构改为下图,使用两个并行化的模块来降低计算量(卷积、池化并行执行,再进行合并)
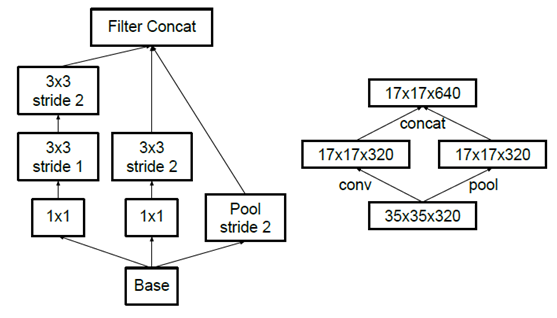
使用 Inception V2 作改进版的 GoogLeNet,网络结构图如下:
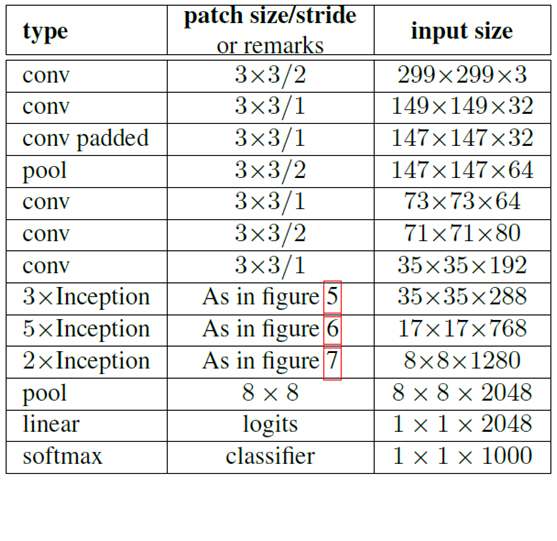
注:上表中的 Figure 5是指小卷积版的 InceptionV2(用 3x3 卷积核代替 5x5 卷积核),Figure 6 是指不对称版的 InceptionV2(用 1xn、nx1 卷积核代替 nxn 卷积核,这里设定 n=7 来应对 17x17 大小的 feature map),Figure 7 指不对称版的 InceptionV2 的变种。
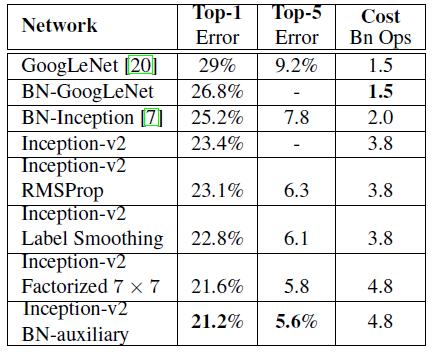
经实验,模型结果与旧的GoogleNet相比有较大提升,如下表所示:
3. Inception V3
“Inception-v3” 概念也出自 GoogLeNet V2 的论文中,原文提到:The last line is referring to all the changes is what we refer to as “Inception-v3” below. 即在卷积和全连接层中都增加了 BN 层。输入被改为 $229 \times 229 \times 3$。关于 GoogLeNet 团队发表的 BN 层的工作请详见 Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift。
Table 3 shows the experimental results about the recognition performance of our proposed architecture (Inception-v2) as described in Section 6. Each Inception-v2 line shows the result of the cumulative changes including the high-lighted new modification plus all the earlier ones. Label Smoothing refers to method described in Section 7. Factorized 7 × 7 includes a change that factorizes the first 7 ×7 convolutional layer into a sequence of 3 ×3 convolutional layers. BN-auxiliary refers to the version in which the fully connected layer of the auxiliary classifier is also batch-normalized, not just the convolutions. We are referring to the model in last row of Table 3 as Inception-v3 and evaluate its performance in the multi-crop and ensemble settings.
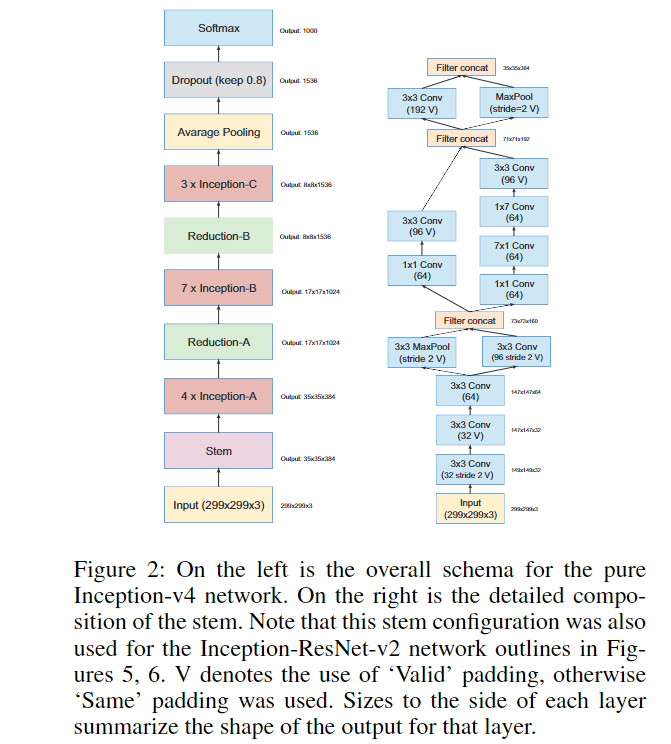
4. Inception V4
Inception V4 研究了 Inception 模块与残差连接的结合,原始论文为 Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning。ResNet 结构大大地加深了网络深度,还极大地提升了训练速度,同时性能也有提升。Inception V4主要利用残差连接(Residual Connection)来改进 V3 结构,得到 Inception-ResNet-v1,Inception-ResNet-v2,Inception-v4 网络。
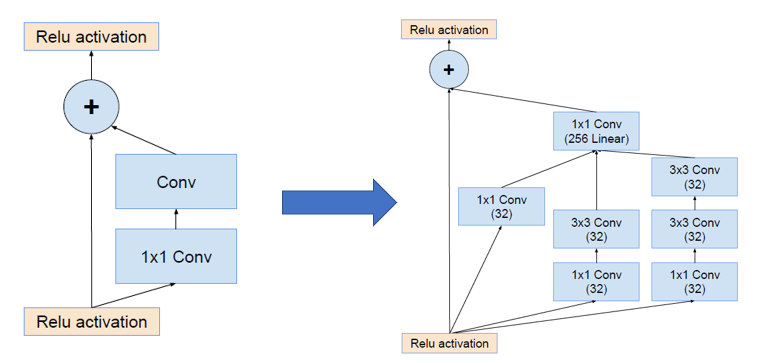
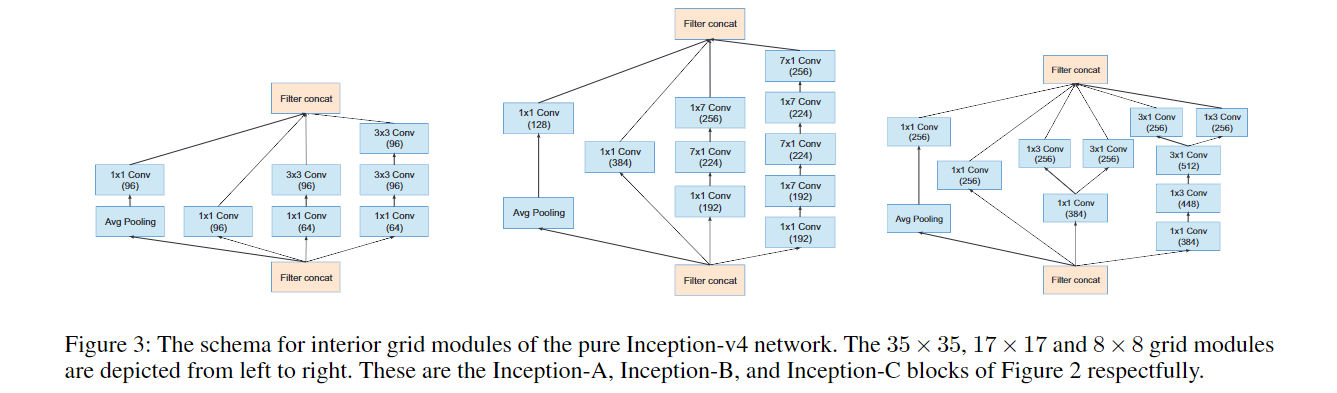
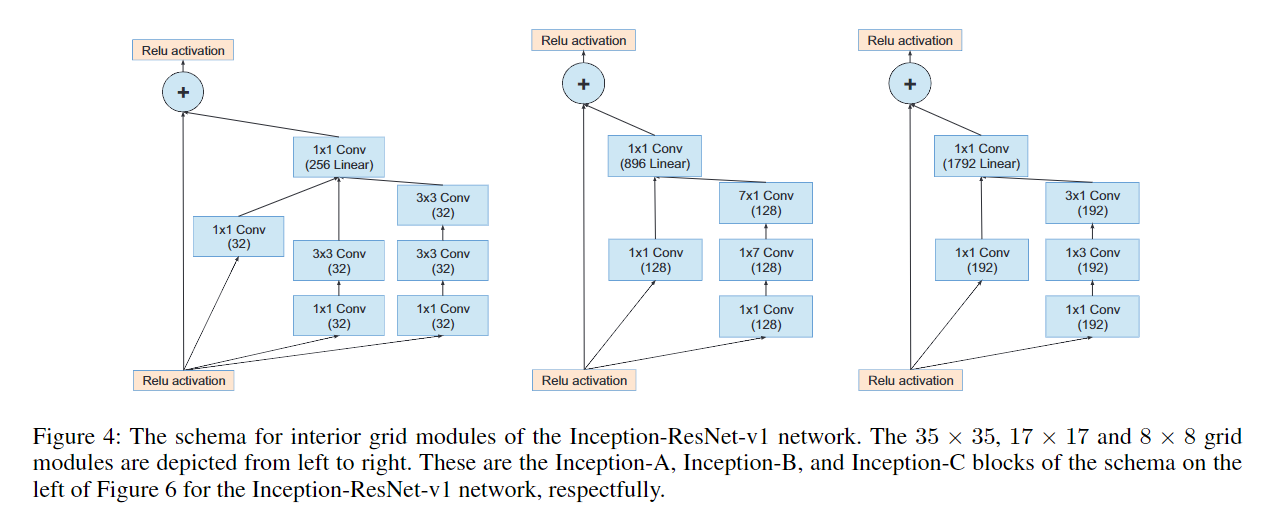
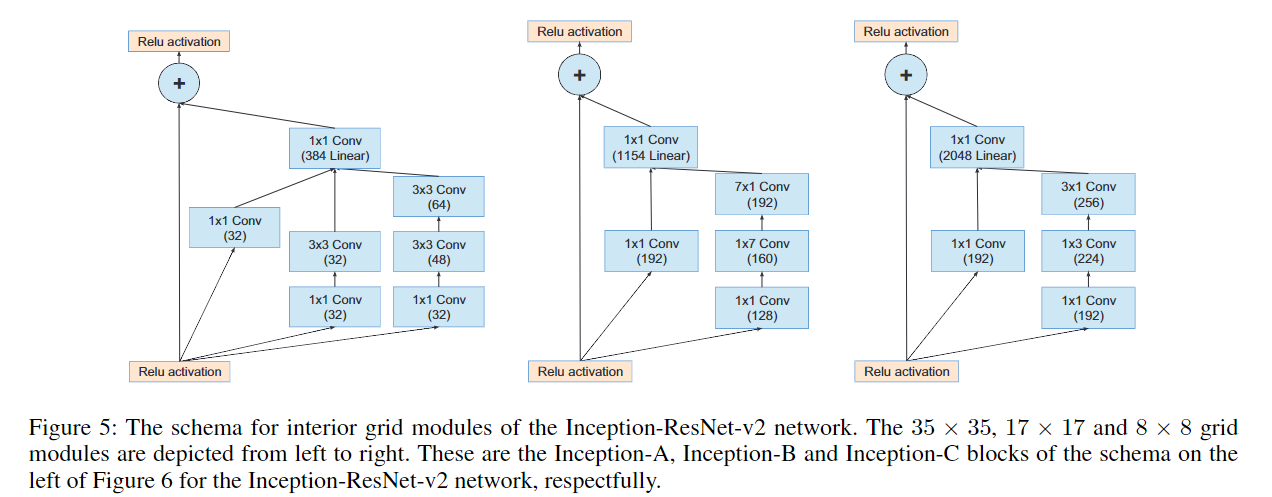
通过20个类似的模块组合,Inception-ResNet 构建如下: